Palladium mud recovery_ Recovery of palladium anode slime_ Palladium containing waste recycling_ Precious metal recycling manufacturers
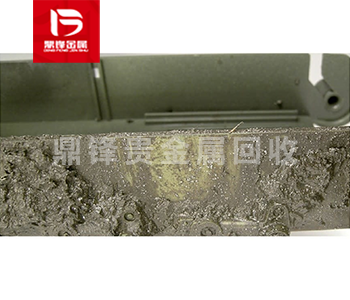
Palladium mud is mainly composed of palladium element, usually containing small amounts of other metals and impurities. Palladium is a typical precious metal with the chemical symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It has a high melting point (1554°C) and boiling point (2963°C), good electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, and is an important industrial catalyst. Palladium mud refers to sediment or solid residue with a high palladium content, usually in the form of gray or black mud. Palladium anode mud is one of the sources of palladium-containing waste recycling. Other sources of palladium-containing waste recycling include palladium water recovery, palladium paste recovery, palladium silver paste recovery, palladium graphite recovery, palladium slag recovery, palladium asbestos recovery, etc.
Product Details
Palladium mud is mainly composed of palladium elements, usually containing small amounts of other metals and impurities. Palladium is a typical precious metal with Chemical symbol Pd and Atomic number 46. It has a high melting point (1554 ℃) and boiling point (2963 ℃), good conductivity and corrosion resistance, and is an important industrial catalyst. Palladium mud refers to sediment or solid residue containing high palladium content, usually in the form of gray or black mud.
The collection methods for palladium mud waste are as follows:
1. Ore mining: Palladium is a rare metal in the Earth's crust that can be found in specific ores. The main method of mining and extracting palladium is through mining and smelting processes. Among them, the byproduct palladium (nickel palladium ore) in nickel ore is one of the important sources.
2. Catalyst recovery: Palladium is widely used in catalysts in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. During the use of the catalyst, palladium gradually reacts with other substances to form sediment, which contains recyclable palladium sludge. By extracting and recycling waste catalysts, a certain amount of palladium sludge can be obtained.
3. Electronic waste: Palladium is increasingly widely used in the electronics industry, especially in circuit boards and connectors. When electronic devices are scrapped or discarded, palladium components can be recycled. By recycling electronic waste, a certain amount of palladium sludge can be obtained.
4. Automotive catalytic converters: Catalysts in automotive catalytic converters typically contain precious metals, including palladium. When a car is scrapped or a catalytic converter is replaced, the palladium in it can be recycled. Recycling automotive catalytic converters is one of the important ways to obtain palladium sludge.
5. Smelting slag: In some smelting processes, especially precious metal smelting processes, the generated slag may contain palladium mud. By extracting and treating these smelting residues, a certain amount of palladium sludge can be obtained.
Palladium anode mud is one of the sources of recycling palladium containing waste, including palladium water recycling, palladium paste recycling, palladium silver slurry recycling, palladium graphite recycling, palladium slag recycling, palladium asbestos recycling, etc. If you have any demand for palladium containing waste recycling, please call our 24-hour service hotline. Dingfeng Precious Metal Recycling and Refining Factory has independent recycling and refining factories without intermediaries to earn price differences. Our professional technical team and customer service personnel provide one-on-one services to ensure customer privacy during the recycling process.